Introduction to SQL, Databases, and RDBMS
What is a Database?
A database is an organized collection of structured information or data, typically stored electronically in a computer system. Databases are designed to efficiently store, retrieve, update, and manage data.
Types of Databases
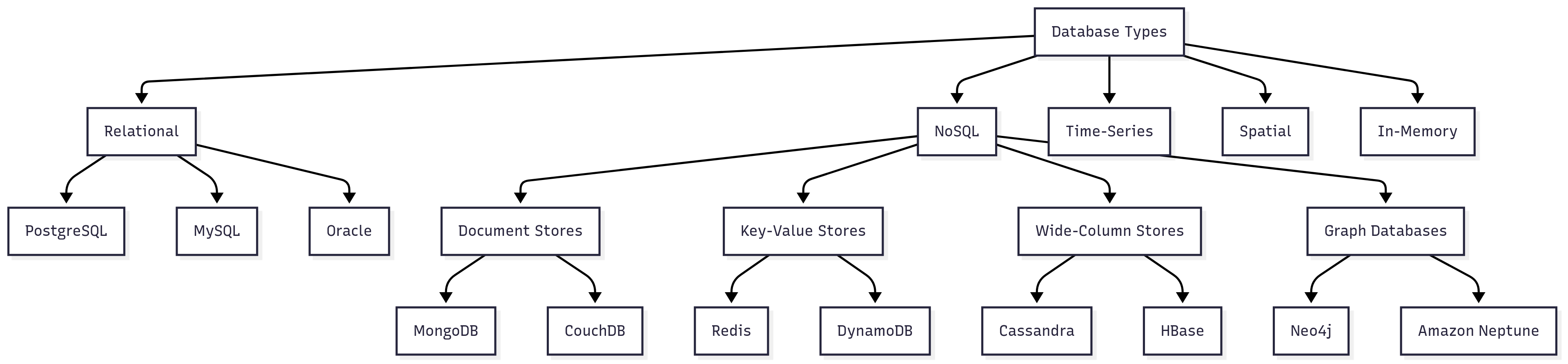
Relational Databases
Relational databases store data in tables with predefined relationships between them. They use Structured Query Language (SQL) for defining and manipulating the data.
Examples: PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, SQLite
NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases provide mechanisms for storage and retrieval of data that are modeled in means other than the tabular relations used in relational databases.
Types of NoSQL databases:
- Document stores: MongoDB, CouchDB
- Key-value stores: Redis, DynamoDB
- Wide-column stores: Cassandra, HBase
- Graph databases: Neo4j, Amazon Neptune
Time-Series Databases
Optimized for time-stamped or time-series data.
Examples: InfluxDB, TimescaleDB (PostgreSQL extension)
Spatial Databases
Optimized for storing and querying spatial data.
Examples: PostGIS (PostgreSQL extension), SpatiaLite
In-Memory Databases
Store data primarily in memory for faster access.
Examples: Redis, Memcached
What is RDBMS?
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is software that:
- Enables users to implement a relational database model
- Manages data stored in tables
- Establishes relationships between data elements
- Provides a structured way to maintain data integrity
- Supports SQL for database operations
What is SQL?
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a domain-specific language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. It allows you to:
- Create, read, update, and delete database records (CRUD operations)
- Create and modify database schema
- Set permissions on database objects
- Execute queries against a database
SQL Categories
| Category | Description | Commands |
|---|---|---|
| Data Definition Language (DDL) | Commands that define the database structure | CREATE, ALTER, DROP, TRUNCATE |
| Data Manipulation Language (DML) | Commands that manipulate data | SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE |
| Data Control Language (DCL) | Commands that control access to data | GRANT, REVOKE |
| Transaction Control Language (TCL) | Commands that control transactions | COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVEPOINT |
Relational Database Concepts
Tables
Tables are the basic storage structure in a relational database. They consist of rows and columns, similar to a spreadsheet.
Columns (Fields)
Columns represent attributes of the entity represented by the table. Each column has a data type that defines what kind of data it can store.
Rows (Records)
Rows contain the actual data values for the entities in the table.
Keys
- Primary Key: Uniquely identifies each record in a table
- Foreign Key: Establishes relationships between tables by referencing the primary key of another table
- Composite Key: A key that consists of multiple columns
Relationships
- One-to-One: One record in table A relates to exactly one record in table B
- One-to-Many: One record in table A relates to multiple records in table B
- Many-to-Many: Multiple records in table A relate to multiple records in table B
Basic SQL Example
Here's a simple example of creating a table and performing basic operations:
-- Create a table
CREATE TABLE employees (
employee_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE,
hire_date DATE,
department VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Insert data
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, email, hire_date, department)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com', '2023-01-15', 'Engineering');
-- Query data
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department = 'Engineering';
-- Update data
UPDATE employees SET department = 'Product Engineering'
WHERE email = 'john.doe@example.com';
-- Delete data
DELETE FROM employees WHERE employee_id = 1;
Practice Problems
Problem 1
Design a simple database schema for a library management system. The system should track books, authors, and borrowers. List the tables you would create, the columns in each table, and how they would relate to each other.
Problem 2
Consider the following scenario: You need to design a database for a small e-commerce website. The website sells products that belong to different categories, and customers can place orders for these products. Write the SQL statements to create the necessary tables for this database, including appropriate primary and foreign keys.
Key Takeaways
- Databases provide organized storage and retrieval of data
- Different types of databases serve different purposes
- RDBMS implements the relational model using tables with rows and columns
- SQL is the standard language for interacting with relational databases
- Understanding database concepts is fundamental to effective data management